Latest Observation
2010.03.31 Wed
Kandy: A Sacred City of Sri Lankan Buddhism
Sri Lanka is famous for its production of tea. Its old name, Ceylon, is a well-known tea brand name as well. The hilly region around Kandy is the birthplace of Ceylon tea.
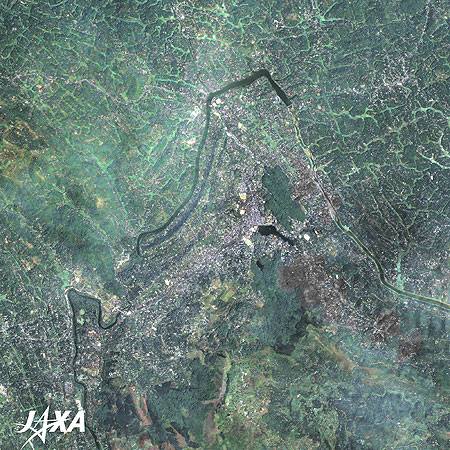
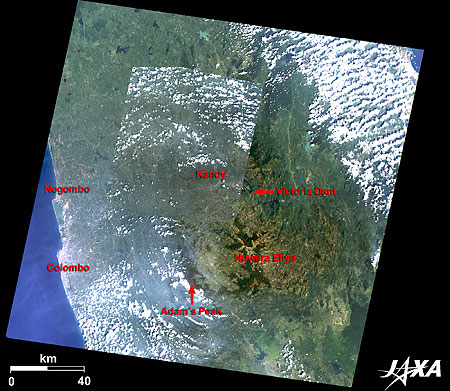
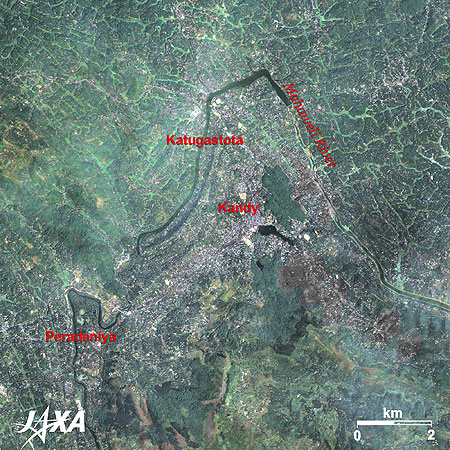
Figure 1 is a mosaic image of Kandy and its surroundings combining images taken by Landsat-7 in January 2006 and by ALOS (Daichi) in January 2009. Although it is located in a tropical region, the central part of Sri Lanka is mountainous—over 1,000 meters above the sea—and has a mild climate. It has plenty of water resources and developed as a tea plantation during the British colonial era. The image depicts the Central Province of Sri Lanka. Kandy and Nuwara Eliya are located in the basin surrounded by mountains. Kandy, the capital of the province, was the last capital of the Sinha royal dynasty. Nuwara Eliya, with a temperate climate all through the year, has developed as the most important location of tea commerce as well as a summer resort.
The name Kandy derives from the Sinhalese “Kanda Uda Pas Rata (the land of mountains).” Europeans (Portuguese) shortened this to “Candea.” The Sinha dynasty settled at Kandy in 1474, after being expelled by invaders from India and pursued to the south. The mountains around Kandy protected the Sinhalese from outside invasion and Kandy prospered for 300 years until it was destroyed by the British.
Kandy was added to the World Heritage List as “Sacred City of Kandy” in 1988.
Figure 2 is an enlarged image of Kandy and its surroundings. Kandy lies about 300 meters above sea level surrounded by mountains in the midst of the narrow basin. Katugastota, located 3 kilometers north along the Mahaweli River, is famous for bathing elephants that are used as a means of transportation.
The Royal Botanical Garden of Peradeniya in the southeast of the city was constructed as a court in the fourteenth century and later became a botanical garden in 1821. The garden is the largest one in Asia, about 600,000 square meters. Over 4,000 kinds of plants grow there, including a tree that was planted by the Japanese Prince and Princess (present Emperor and Empress).
caption on
caption off
Fig. 3. Enlarged Image of Kandy
Kandy (kmz, 5.12 MB, Low Resolution) as seen on Google Earth
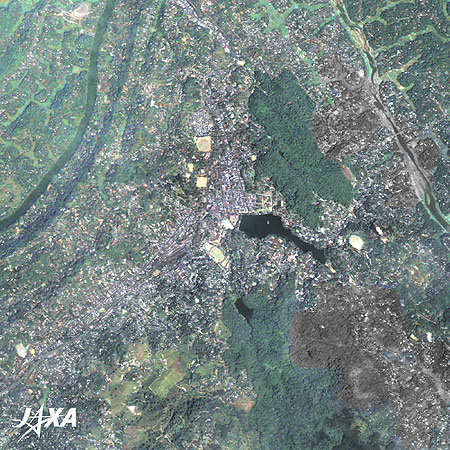
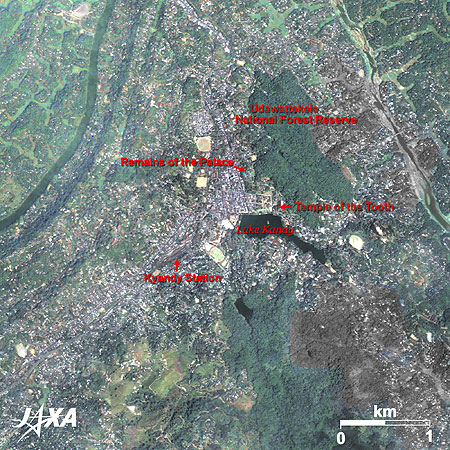
Figure 3 is an enlarged image of Kandy. Artificial Lake Kandy is seen at the center of the image. It was constructed by Sri Vikrama Rajasinha, the last king of the Sinha Dynasty. It took 12 years to complete. The city developed north and west of the lake.
The Temple of the Tooth and the remains of the palace are located north of the lake. The Temple of the Tooth is the most renowned temple in Sri Lanka and famous for housing the relic of the tooth of Buddha. It is said that when Buddha was cremated in India in 543 B.C., his tooth was retrieved and brought to Sri Lanka.
Udawattekele National Forest Reserve north of the temple is a sanctuary famous for its many kinds of exotic birds. Public facilities are concentrated west of the lake.
Relic of the Tooth of Buddha
According to Sri Lankan legend, the relic of the tooth was brought to Sri Lanka in the fourth century. The relic then became a symbol of the royal throne of Sri Lanka. Some wars were fought to possess the relic. The Temple of the Tooth was built by the Sinha Dynasty in the sixteenth century to worship the relic. A festival started in the eighteenth century to display the relic. This festival is called Perahera and is held every summer. Elephants, deemed as the sacred animal, are gathered from all parts of the country and about 100 of them parade the streets following the elephant that carries the relic. At the climax of the festival, thousands of people dance around the parade of the elephants.
Explanation of the Images:
| Satellite: | Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) (Daichi) |
| Sensor: | Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer-2 (AVNIR-2) and Panchromatic Remote-sensing Instrument for Stereo Mapping (PRISM) |
| Date: |
0512 (UTC) on January 29, 2009 (AVNIR-2) 0512(UTC) on March 11, 2007 (PRISM) |
| Ground resolution: | 10 m (AVNIR-2) and 2.5 m (PRISM) |
| Map Projection: | Universal Transversal Mercator (UTM) |
AVNIR-2 has four observation bands. The color composite images are usually produced by assigning red to Band 3 (610 to 690 nm), green to Band 2 (520 to 600 nm) and blue to Band 1 (420 to 500 nm). The resulting images have natural coloring as if seen by the naked eye. Each color indicates the following ground objects:
| Dark Green: | Forests |
| Bright Green: | Farmlands, Grass fields |
| Light Bluish-grey: | Urban areas |
| Brown: | Bare grounds |
| White: | Buildings or clouds |
| Blue: | Sea or lake |
PRISM is an optical sensor for observing ground surfaces with visible and near-infrared signals in the 520- to 770-nanometer (one-billionth of a meter) band. The image is monochromatic but has a higher resolution. PRISM has three independent optical systems to acquire images in the view of nadir, forward, and backward simultaneously. Only the nadir images are used in these figures.
The above AVNIR-2 color composite image is decomposed into, hue, saturation, and intensity. The intensity portion is replaced by PRISM data. The hue, saturation, and intensity data are then reversed into a color image. This color image has a virtual 2.5-m resolution. A color image composed by combining a higher resolution monochromatic image and a lower resolution color image is called a pan-sharpened image.
Some parts of Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 are seen black and white, since those parts of the AVNIR-2 image are covered by clouds and replaced by the PRISM image. Therefore, those parts are not colored.
| Satellite: | Landsat-7 (USA) |
| Sensor: | Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) |
| Date: | January 23, 2006 (Fig. 1)) |
| Ground resolution: | 30 m |
| Map Projection: | Universal Transversal Mercator (UTM) |
This image data is downloaded from the Global Land Facility (GLCF) Earth Science Data Interface site at the University of Maryland free of charge. The color composite image is produced by assigning red to Band 3 (630 to 690 nm), green to Band 2 (520 to 600 nm) and blue to Band 1 (450 to 520 nm). The resulting image has natural coloring as if seen by the naked eye.
Related Sites
Search by Year
Search by Categories
Tags
-
#Earthquake
-
#Land
-
#Satellite Data
-
#Aerosol
-
#Public Health
-
#GCOM-C
-
#Sea
-
#Atmosphere
-
#Ice
-
#Today's Earth
-
#Flood
-
#Water Cycle
-
#AW3D
-
#G-Portal
-
#EarthCARE
-
#Volcano
-
#Agriculture
-
#Himawari
-
#GHG
-
#GPM
-
#GOSAT
-
#Simulation
-
#GCOM-W
-
#Drought
-
#Fire
-
#Forest
-
#Cooperation
-
#Precipitation
-
#Typhoon
-
#DPR
-
#NEXRA
-
#ALOS
-
#GSMaP
-
#Climate Change
-
#Carbon Cycle
-
#API
-
#Humanities Sociology
-
#AMSR
-
#Land Use Land Cover
-
#Environmental issues
-
#Quick Report
Related Resources
Related Tags
Latest Observation Related Articles
-
 Latest Observation 2025.12.03 Wed [Quick Report] Analysis results from satellite precipitation data on the record-breaking heavy rainfall occurring in Southeast Asia in late November 2025
Latest Observation 2025.12.03 Wed [Quick Report] Analysis results from satellite precipitation data on the record-breaking heavy rainfall occurring in Southeast Asia in late November 2025 -
 Latest Observation 2025.10.01 Wed [Quick Report] Hurricane Humberto “Eye” captured by EarthCARE satellite (Hakuryu)
Latest Observation 2025.10.01 Wed [Quick Report] Hurricane Humberto “Eye” captured by EarthCARE satellite (Hakuryu) -
 Latest Observation 2025.02.28 Fri The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, may have run aground on the continental shelf of South Georgia:
Latest Observation 2025.02.28 Fri The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, may have run aground on the continental shelf of South Georgia:
The trajectory of iceberg A23a observed by “GCOM-W”, “ALOS-2” and “ALOS-4” -
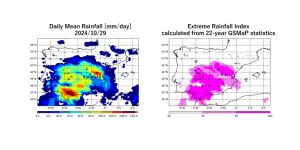 Latest Observation 2024.11.06 Wed [Quick Report] Heavy rainfalls in eastern Spain, as seen by the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP)
Latest Observation 2024.11.06 Wed [Quick Report] Heavy rainfalls in eastern Spain, as seen by the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP)