
Meteorology and the Environment
2012.01.11 Wed
Climate anomalies in Australia (2002 to 2010)
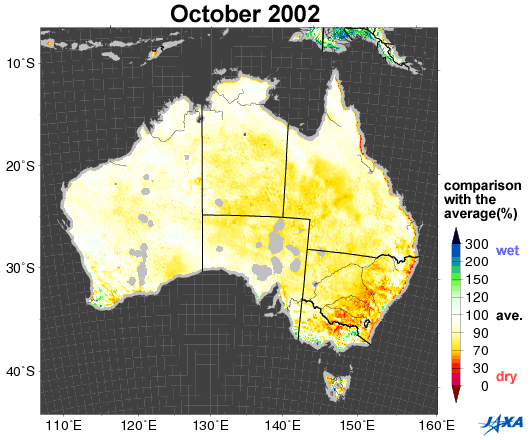
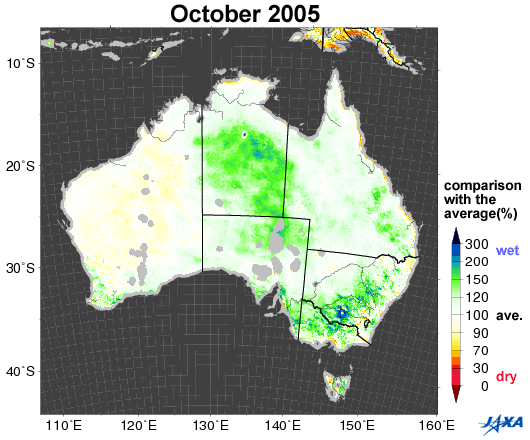
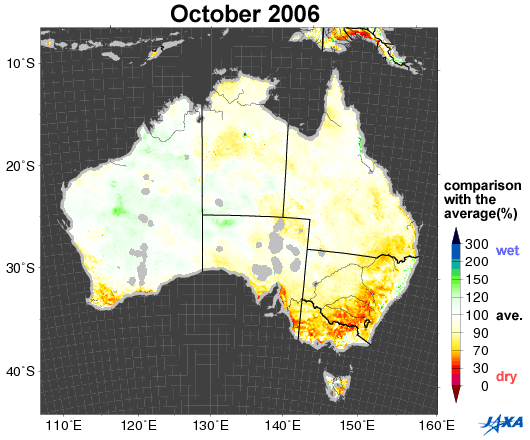
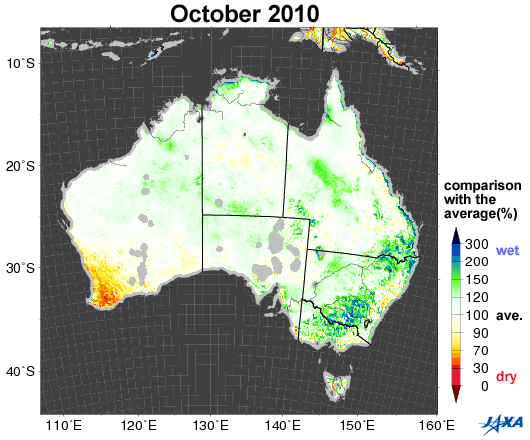
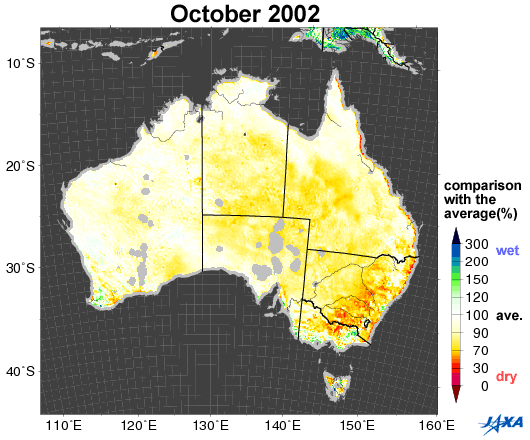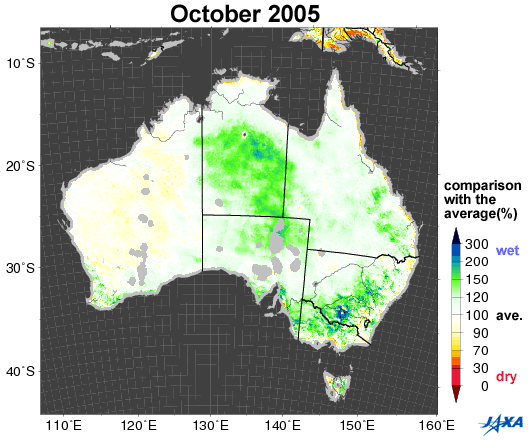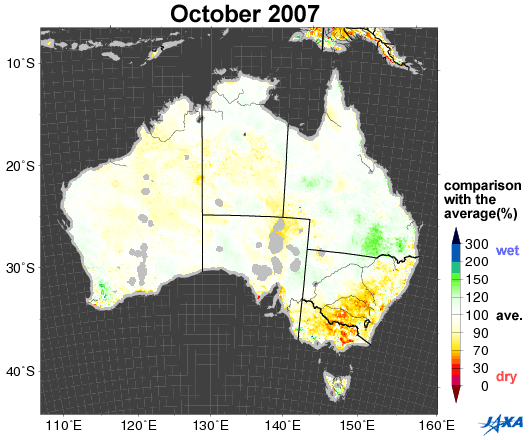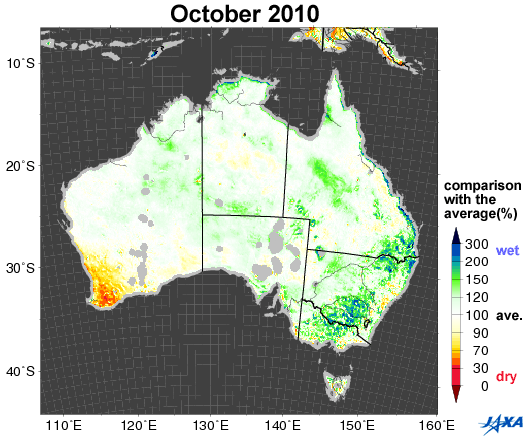
Fig.1. Changes in soil moisture in Australia (October 2002, 2005, 2006, 2010)
Yellow to red shows areas that are drier than the average
Figure 1 shows a comparison between the average values of soil moisture*1 (2002 to 2010) in Australia and the values corresponding to October 2002, 2005, 2006, and 2010, as observed by the Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS (AMSR-E)*2. Areas colored yellow to red are drier than the average.
Australia suffered severe droughts from 2002 to 2003. A long drought in 2006 was particularly severe in historical terms. As shown in Figure 1, the southeastern area was wet in 2005 and 2010, but became drier in 2002 and 2006.
Australia’s land area is 7.7 million km2, around twenty times that of Japan (0.38 million km2). Over half of the Australian land area is used for agriculture, but the cultivated land accounts for 0.24 million km2, which accounts for just 6% of the agricultural land and 3% of the total land. Over 90% of agricultural land is used for pasturage of beef cattle and sheep. Crops are planted in the states of Western Australia and New South Wales, located in the southwest and southeast of the country, respectively. Pastures are spread over large areas in the state of Queensland, in the northeastern part of the country.
*1) Soil moisture represents the proportion of moisture contained in a unit volume of soil. When soil absorbs moisture and reaches saturation, the soil moisture is around 50%.
*2) ASMR-E was developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and is onboard NASA’s Earth-observing satellite, Aqua. It was launched in 2002 and had since collected data of ocean surface temperature, precipitation, soil moisture, and ice caps in the Arctic Ocean. On October 4, 2011, the AMSR-E observation and antenna rotation automatically halted because the antenna rotation friction had reached the limit (40 rotations per minute) necessary for regular observations.
Comparison of October soil moisture with the average October soil moisture for 2002-2010
Figure 2 shows yearly changes in soil moisture in October from 2002 to 2010. AMSR-E images indicate the dryness of the soil in 2002 and successive years from 2006. Wheat is the main crop in Australia and is planted over half the cultivated land. The major areas under wheat cultivation are located in the southwest and east of the country, and they correspond to the areas that suffered severe dryness during the study period.
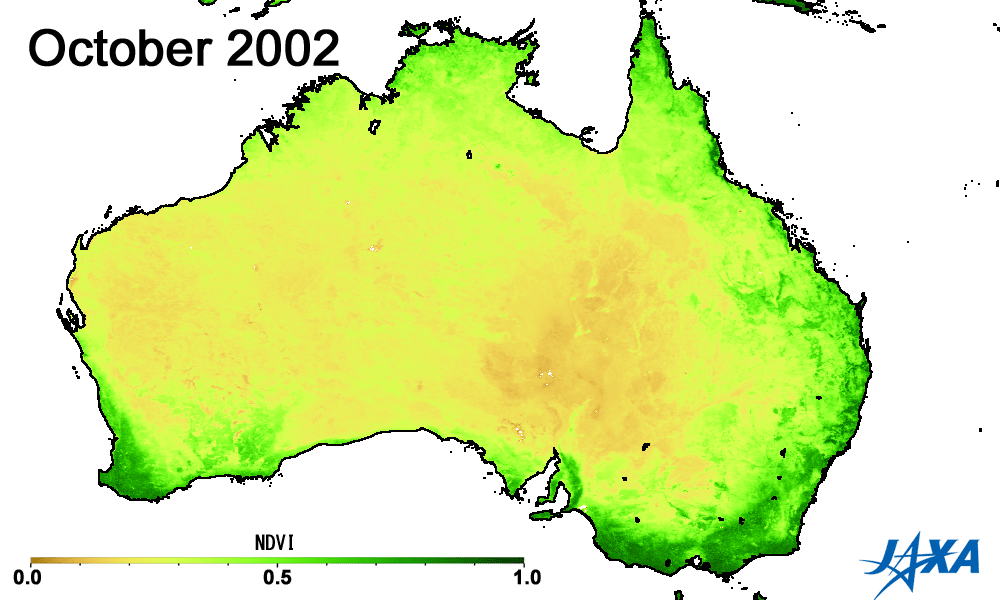
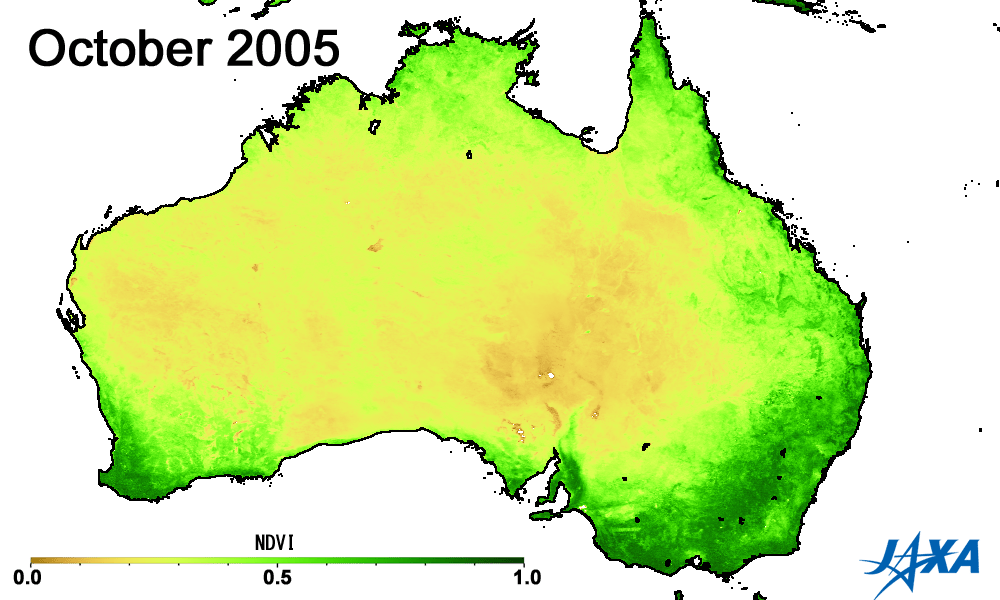
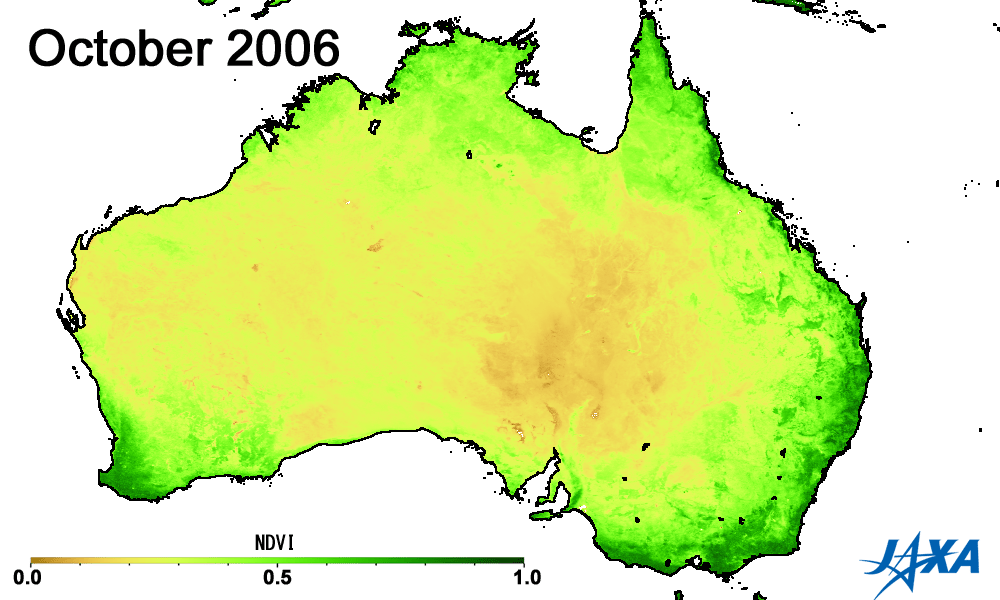
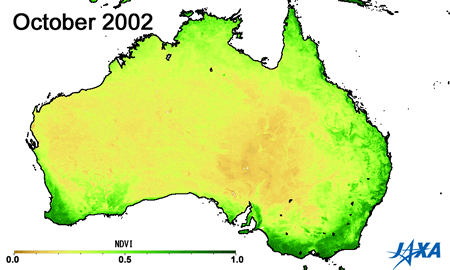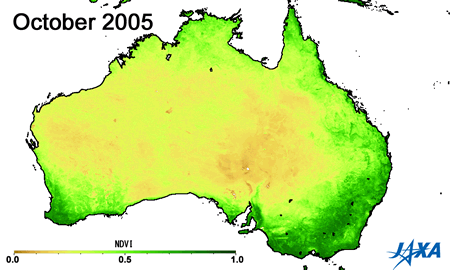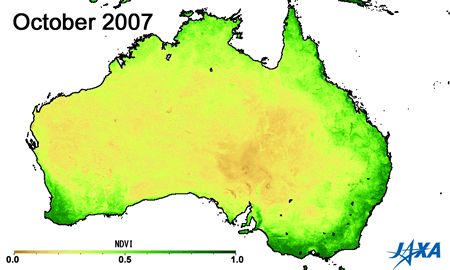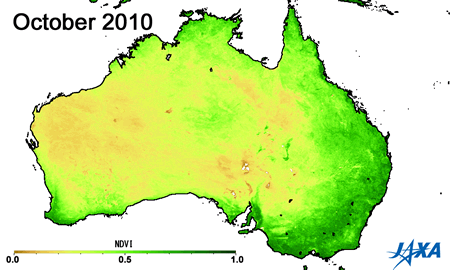
Green indicates greater plant activity
Figures 3 and 4 show the vegetation index*3 obtained from observations made by MODIS aboard the American Earth observing satellite, TERRA. The area of high vegetation activity (shown in green) is small in 2002 and 2006 but large in 2005 and 2010. The vegetation index can help determine areas of low soil moisture and droughts.
*3) A higher vegetation index indicates increased health and activity of vegetation.
Historically, droughts have occurred in Australia every 10 years. However, Australia had been thrice hit by drought (2002, 2006, and 2007) since 2000. In particular, the drought of 2006 was the worst such even in the past 100 years. Australia has vast land areas and mixed climates. Droughts happen frequently in some areas, whereas other areas are hit by floods.
The recent abnormal climate results in a reduction in the supply of grains, leading to increase in the demand for grain. Therefore, the decrease in crops due to the drought in Australia accelerates the global food crisis. Crop yields during 2002 and 2006 were half of the average. The Australian government has prioritized measures to increase the productivity and to counteract the effects of climate change.
Explanation of the Images:
| Satellite: | Earth Observing System, Aqua, NASA |
| Sensor: | Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer for EOS (AMSR-E) |
| Date: | October 2002 to October 2010 (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2) |
| Satellite: | Earth Observing System, Terra, NASA |
| Sensor: | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), NASA |
| Date: | October 2002 to October 2010 (Fig. 3 and Fig. 4) |
Related Sites
・Wave of Fresh Green Coloring the Northern Hemisphere
・Japan Island during “Golden Week” observed from space
Search by Year
Search by Categories
Tags
-
#Earthquake
-
#Land
-
#Satellite Data
-
#Aerosol
-
#Public Health
-
#GCOM-C
-
#Sea
-
#Atmosphere
-
#Ice
-
#Today's Earth
-
#Flood
-
#Water Cycle
-
#AW3D
-
#G-Portal
-
#EarthCARE
-
#Volcano
-
#Agriculture
-
#Himawari
-
#GHG
-
#GPM
-
#GOSAT
-
#Simulation
-
#GCOM-W
-
#Drought
-
#Fire
-
#Forest
-
#Cooperation
-
#Precipitation
-
#Typhoon
-
#DPR
-
#NEXRA
-
#ALOS
-
#GSMaP
-
#Climate Change
-
#Carbon Cycle
-
#API
-
#Humanities Sociology
-
#AMSR
-
#Land Use Land Cover
-
#Environmental issues
-
#Quick Report
-
#GOSAT-GW
Related Resources
Meteorology and the Environment Related Articles
-
 Meteorology and the Environment 2025.11.05 Wed The Breakup of the World’s Largest Iceberg, “A23a”: The Trajectory of Iceberg A23a Observed by “GCOM-W”, “ALOS-2”, “ALOS-4” and the Latest Satellite, “GOSAT-GW”
Meteorology and the Environment 2025.11.05 Wed The Breakup of the World’s Largest Iceberg, “A23a”: The Trajectory of Iceberg A23a Observed by “GCOM-W”, “ALOS-2”, “ALOS-4” and the Latest Satellite, “GOSAT-GW” -
 Meteorology and the Environment 2025.05.20 Tue February 2025: Global Sea Ice Extent Reaches its Lowest in the History of Satellite Observations
Meteorology and the Environment 2025.05.20 Tue February 2025: Global Sea Ice Extent Reaches its Lowest in the History of Satellite Observations -
 Meteorology and the Environment 2023.10.11 Wed Climate Change 2023 (2) : Antarctic Winter Sea Ice Extent Lowest Ever Recorded
Meteorology and the Environment 2023.10.11 Wed Climate Change 2023 (2) : Antarctic Winter Sea Ice Extent Lowest Ever Recorded -
 Meteorology and the Environment 2023.08.31 Thu Climate Change 2023 (1) : Sea Surface Temperature Rise and El Niño Event
Meteorology and the Environment 2023.08.31 Thu Climate Change 2023 (1) : Sea Surface Temperature Rise and El Niño Event