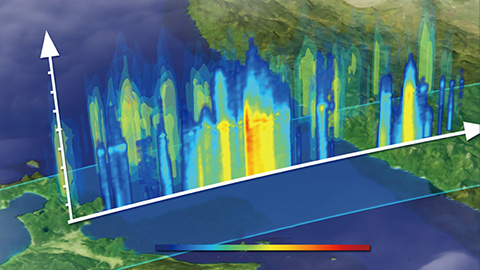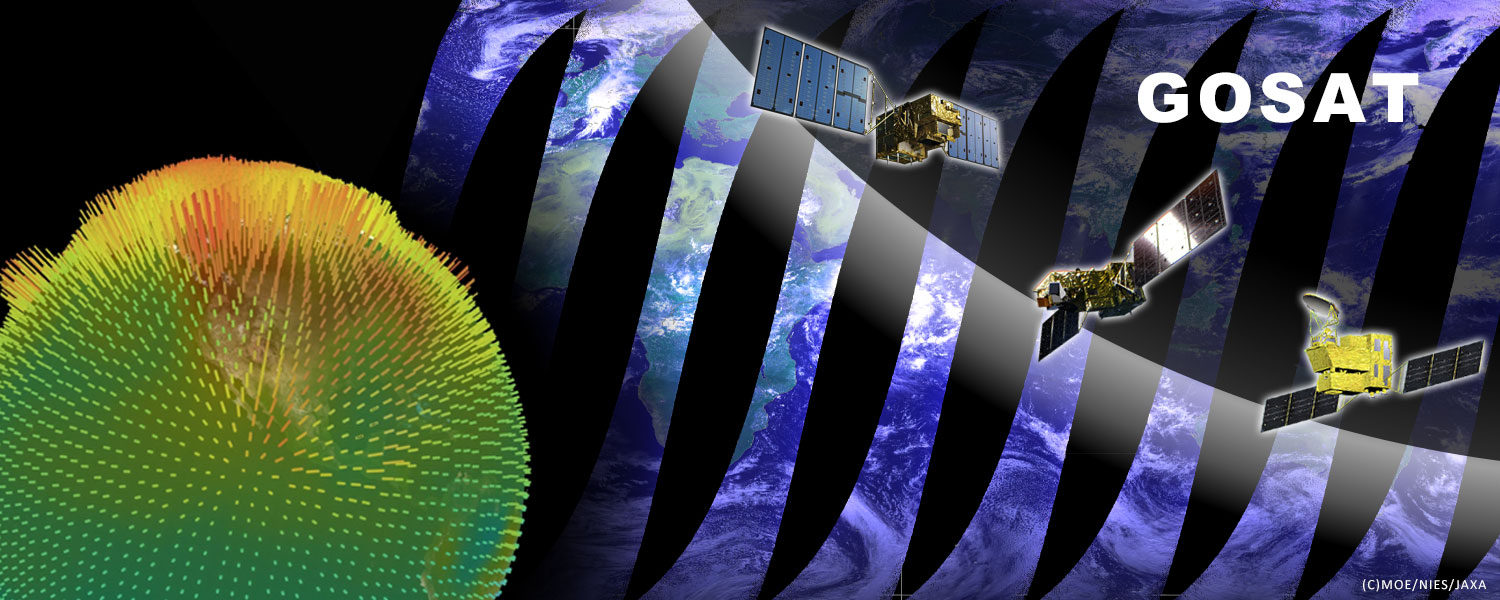
GOSAT project is conducting research and development and data calibration and validation by using sensors onboard the “IBUKI” (GOSAT) series satellites for observing greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane) which are the causes of global warming.
By onboarding a sensor on earth observation satellite, it is able to measure greenhouse gas distribution at more than 56,000 points on the earth and observe more than 100 times as many observation points placed around the world every three days.
JAXA is contributing to international efforts to combat global warming by monitoring the distribution and temporal changes of greenhouse gases on the globe and improving accuracy of estimating greenhouse gas emissions and estimating the sources of greenhouse gases emissions.
Related main satellites and sensors
| Satellites | Main sensors | Observation period |
|
Global Observing SATellite for Greenhouse gases and Water cycle “IBUKI GW” (GOSAT-GW)
|
Total Anthropogenic and Natural emissions mapping SpectrOmeter-3 | JFY2025- |
| Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite “IBUKI-2” (GOSAT-2) | Thermal and Near Infrared Sensor for Carbon Observation Fourier-Transform Spectrometer-2 (TANSO-FTS-2) TANSO Cloud and Aerosol Imager-2 (TANSO-CAI-2) |
2018- (in operation) |
| Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite “IBUKI” (GOSAT) | Thermal And Near infrared Sensor for carbon Observation Fourier-Transform Spectrometer (TANSO-FTS) TANSO Cloud and Aerosol Imager (TANSO-CAI) |
2009-(in operation) |
* GOSAT is a joint project of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the Ministry of the Environment (MOE) and the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES)