The Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) and the Coordination Group on Meteorological Satellites (CGMS) recognize that high-quality, systematic observations of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) from a constellation of space-based sensors can make critical contributions to an integrated global greenhouse gas (GHG) observing system. They therefore directed the joint CEOS-CGMS Working Group on Climate (WGClimate) to formulate a roadmap to implement a constellation architecture for monitoring CO2 and CH4 from space. The primary objective of this GHG Roadmap is to coordinate efforts across CEOS and CGMS agencies to maximise the quality, utility, transparency and continuity of space-based GHG products for science and policy applications. Its ultimate goal is to facilitate the development of fit-for-purpose operational systems that integrate space-based GHG estimates with ground-based, airborne and shipborne observations of CO2 and CH4 to address the needs of a diverse range of stakeholders.
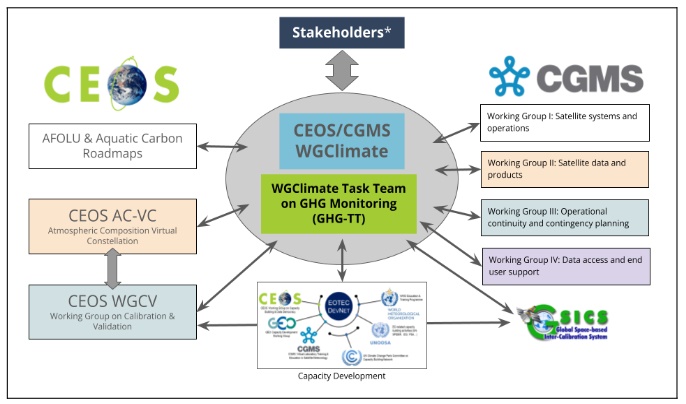 CEOS, CGMS and WMO GSICS entities currently included in the task team.
CEOS, CGMS and WMO GSICS entities currently included in the task team.
The first issue of the CEOS/CGMS GHG Roadmap focused on delivering space-based CO2 and CH4 products to support the Paris Agreement’s Global Stocktakes (GSTs). This issue of the roadmap continues to support that goal, but has been updated to accommodate lessons learned from the first GST. Its scope has also been expanded to support the rapid evolution of the international GHG science, inventory, policy and regulatory communities. Changes include:
- An enhanced focus on engagement and co-development with stakeholders in the international science, inventory, policy, and regulatory communities;
- Ongoing efforts to engage with new partners, including the World Meteorological Organization Global Greenhouse Gas Watch (WMO G3W) and United Nations Environment Programme International Methane Emissions Observatory (UNEP IMEO);
- An updated summary of the evolving requirements and capabilities for space-based measurements that can quantify CO2 and CH4 concentrations and support flux estimation;
- Updates to the space-based CO2 and CH4 monitoring architecture, broadening the focus from regional-scale, global mapping missions to include both public sector and non-governmental (New Space) missions that can monitor emissions at facility scales;
- A brief review of the research needed to derive CO2 and CH4 concentrations from space-based measurements, validate these results against internationally recognized standards, and then use them to derive budgets of CO2 and CH4 on spatial scales spanning individual facilities to nations;
- Efforts needed to foster the transition from research to operations (R2O) to support the development of an operational GHG Monitoring and Verification Support (GHG MVS) system that serves stakeholders in the science, inventory, policy and regulatory communities; and
- An explicit focus on capacity building to foster the use of space-based GHG products.
 Stakeholders and their interactions.
Stakeholders and their interactions.
The updated roadmap describes specific thematic areas where CEOS and CGMS are working with stakeholders and partners to co-develop improved, fit-for-purpose space-based GHG products. It then summarises the relative roles of the joint CEOS-CGMS WGClimate GHG Task Team and other CEOS and CGMS teams in its implementation. As in the first issue, detailed activities and action items, which are continuously evolving, are described in an Annex. With these changes, the GHG Roadmap should foster the coordination of space-based GHG products that better address the needs of an increasingly diverse stakeholder community and be more resilient to the future evolution of this rapidly evolving field.
 We are now pleased to announce that at the recent 38th CEOS Plenary, the principals have unanimously endorsed this update to the Greenhouse Gas Roadmap. Several CEOS agencies explicitly recognized the remarkable team effort that made this swift update possible and it was commented as “CEOS at its best!”.
We are now pleased to announce that at the recent 38th CEOS Plenary, the principals have unanimously endorsed this update to the Greenhouse Gas Roadmap. Several CEOS agencies explicitly recognized the remarkable team effort that made this swift update possible and it was commented as “CEOS at its best!”.
Simultaneously, in coordination with the CGMS Secretariat, endorsement was requested from the CGMS principals. We are delighted to share that also CGMS unanimously endorsed the update on the same day as CEOS. With endorsements from both CEOS and CGMS, Issue 2 is now fully approved and officially released to the public. We stimulate you to share the roadmap within your network and community. The final version is now available here, which can be found under two public CEOS pages:
https://ceos.org/publications-key-documents/
https://ceos.org/ourwork/workinggroups/climate/ghg-tt/
We look forward to implement the efforts needed to transition the current framework from research to operations. This will support sustained and operational GHG Monitoring and Verification Support systems that serve stakeholders across science, inventory, policy, and regulatory communities, including a focus on the required capacity building promoting the wider use of space-based GHG products.

Yasjka Meijer (ESA)
GHG Task Team Lead in WGClimate